How to Improve User Experience with AI: A guide for UX/UI designers
This guide breaks down AI's role in personalization, predictive design, and automation, showing you how to create exceptional user journeys.
UX is a powerful tool that can revolutionize how we design and deliver experiences. If you're a UX/UI designer, it's time to partner with AI in creating exceptional user journeys.
This guide will explore how AI can be your secret weapon, helping you craft more intuitive, personalized, and delightful products.
Understanding AI's Role in UX/UI Design
AI's ability to analyze data, learn patterns, and make predictions is a great help for UX/UI designers, if explored wisely.
Personalization at Scale: AI can tailor experiences to individual users based on their behavior, preferences, and past interactions.
Predictive Design: By analyzing user data, AI can anticipate user needs, making interfaces more intuitive.
Automation of Repetitive Tasks: AI can handle routine design tasks, freeing you up for more strategic and creative work.
Enhanced Accessibility: AI can help create more inclusive designs by adapting interfaces for users with different abilities.
Data-Driven Insights: AI-powered analytics can provide deep insights into user behavior, informing design decisions.
Key Ways to Integrate AI into Your UX/UI Workflow
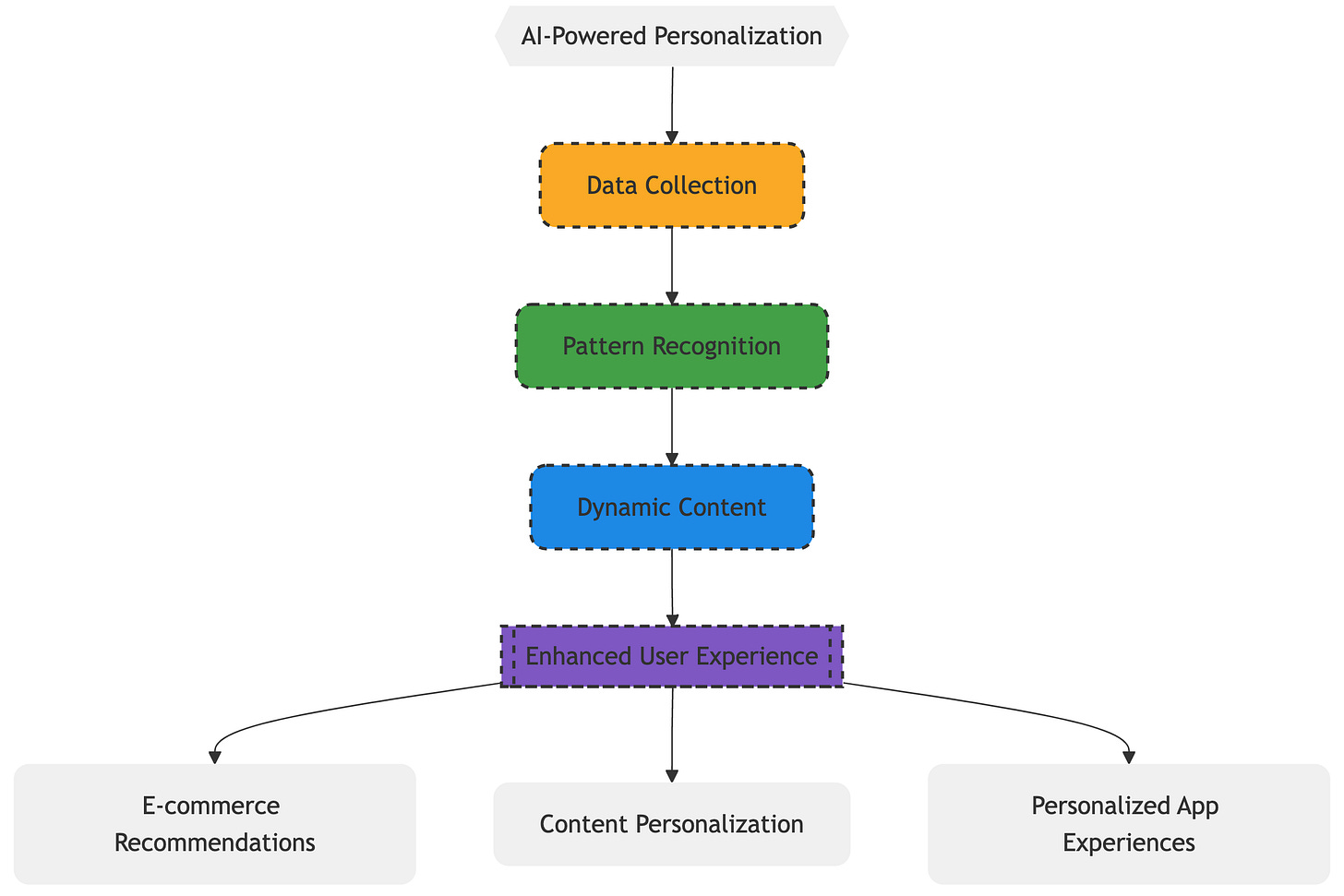
1. AI-Powered Personalization
Users want experiences that feel tailored to their needs and preferences. AI makes it possible to deliver this level of personalization at scale:
How it works:
Data Collection: AI gathers data on user behavior, such as clicks, browsing history, purchase patterns, and interactions with the product.
Pattern Recognition: Machine learning algorithms identify patterns and segment users based on their behavior and preferences.
Dynamic Content: AI dynamically adjusts the user interface, content, and recommendations based on each user's profile.
Examples:
E-commerce: Amazon's recommendation engine suggests products based on your browsing and purchase history. Similarly, Netflix personalizes movie recommendations.
Content Platforms: Spotify curates personalized playlists like "Discover Weekly" based on your listening habits.
Personalized App Experiences: Duolingo adapts language lessons to your learning pace and style.
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
Over-Personalization: Too much personalization can feel intrusive or creepy 🫣. Strike a balance between relevance and privacy.
Ignoring User Control: Always give users the option to customize their experience and opt out of personalization features.
Data Bias: Ensure your training data is diverse and representative to avoid biased or discriminatory outcomes.
Things to Watch Out For:
Data Privacy: Be transparent about how you collect and use user data. Comply with privacy regulations like GDPR.
Algorithm Transparency: Users should understand why they see specific content or recommendations.
User Feedback: Continuously collect user feedback to refine your personalization algorithms.
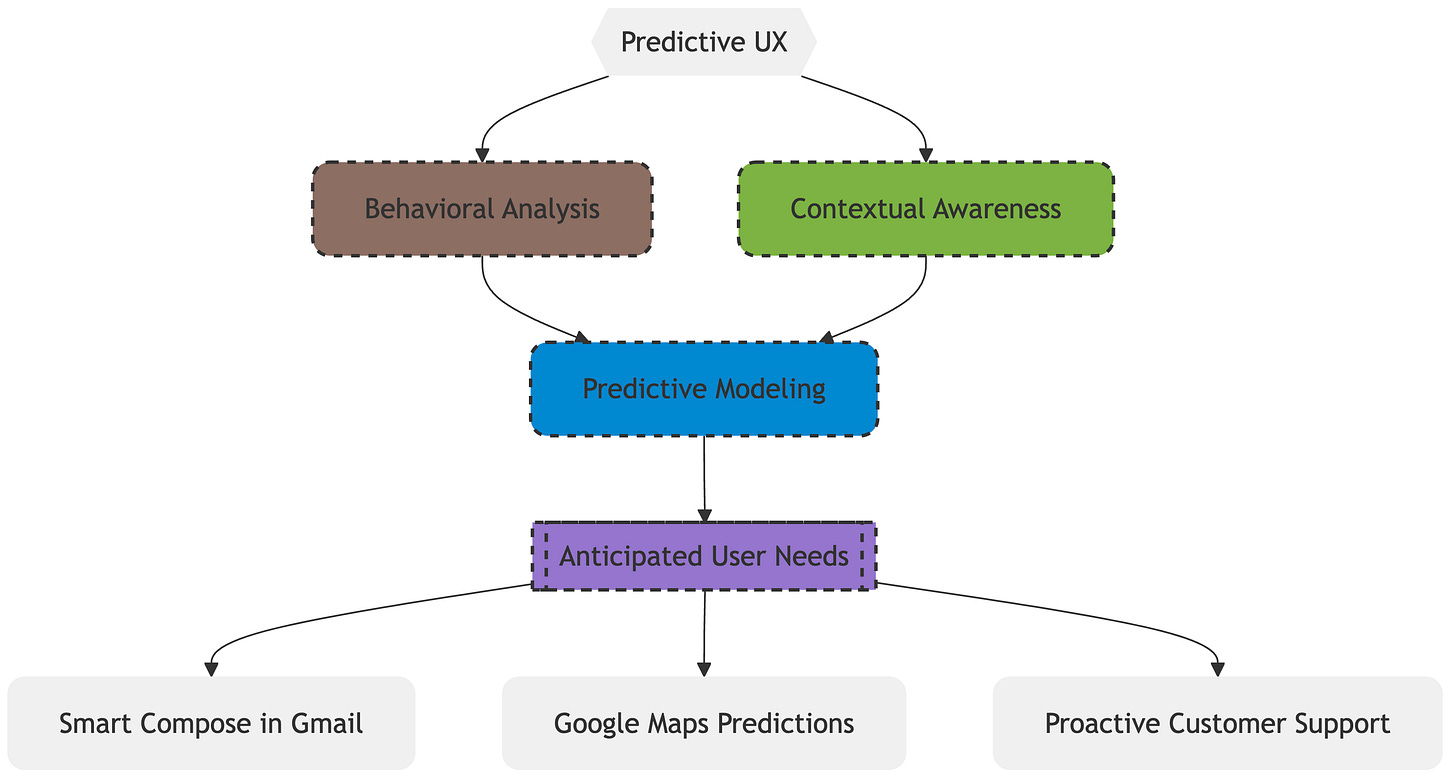
2. Predictive UX: Anticipating User Needs
Imagine an interface that knows what you want before you even ask 🤯. That's the power of predictive UX. By analyzing user data and behavior, AI can anticipate user needs and proactively offer relevant information or actions.
How it Works:
Behavioral Analysis: AI tracks user interactions to understand their goals, pain points, and typical workflows.
Contextual Awareness: AI considers factors like time of day, location, and device to provide contextually relevant suggestions.
Predictive Modeling: Machine learning models predict future user actions based on past behavior and contextual data.
Examples:
Smart Compose in Gmail: Predicts and suggests complete sentences as you type.
Google Maps: Predicts your destination based on your routine and offers navigation suggestions.
Proactive Customer Support: AI chatbots can anticipate common user issues and offer solutions before the user contacts support.
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
Inaccurate Predictions: False predictions can be frustrating and erode user trust.
Lack of Context: Predictions should be based on a holistic understanding of the user's context, not just isolated data points.
Over-Reliance on Automation: Predictive features should assist, not replace, user control.
Things to Watch Out For:
Continuous Learning: Ensure your AI models are continuously learning and adapting to changing user behavior.
User Validation: Test your predictions with real users to ensure accuracy and relevance.
Error Handling: Design for graceful failure. If a prediction is wrong, provide an easy way for users to correct it or dismiss it.
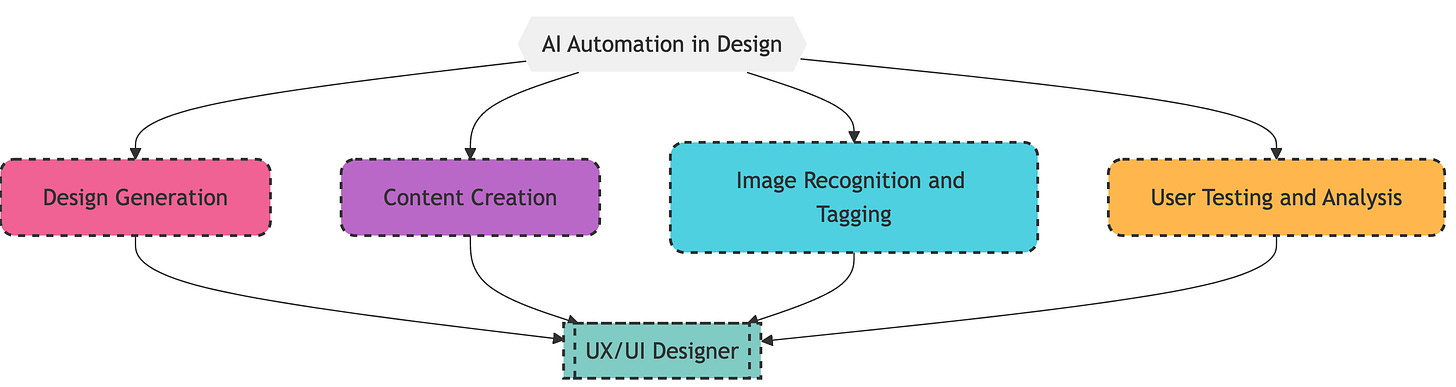
3. Automating Design Tasks with AI
AI can be your design assistant, handling repetitive tasks and freeing you up for more creative work.
How it Works:
Design Generation: AI can generate design variations, layouts, and even color palettes based on your input.
Content Creation: AI can help with writing microcopy, generating product descriptions, or even creating basic graphics.
Image Recognition and Tagging: AI can automatically tag images, making it easier to organize and search your design assets.
User Testing and Analysis: AI can analyze user feedback, identify patterns, and suggest design improvements.
Examples:
Khroma: An AI-powered color palette generator that learns your preferences.
Uizard: Turns hand-drawn sketches into digital designs and prototypes.
Copy.ai: Helps generate marketing copy, product descriptions, and social media content.
Hotjar: Uses AI to analyze user behavior and provide heatmaps, session recordings, and feedback polls.
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
Over-Reliance on AI-Generated Designs: AI should be a tool, not a replacement for human creativity.
Lack of Customization: Don't accept AI-generated designs blindly. Customize and refine them to fit your brand and user needs.
Ignoring User Feedback: AI-generated designs should still be tested with real users.
Things to Watch Out For:
Quality Control: Ensure AI-generated content and designs meet your quality standards.
Brand Consistency: AI-generated elements should align with your brand guidelines.
Ethical Considerations: Be mindful of potential biases in AI-generated content and designs.
Advices and Tips for Implementing AI in UX/UI
Start Small, Think Big: You don't have to overhaul your entire design process overnight. Begin with a small AI-powered feature and gradually expand as you learn and gather data.
Focus on User Value: Always prioritize user needs and pain points. Ask yourself: How can AI enhance the user experience and solve real problems?
Collaborate with Data Scientists and Developers: Successful AI implementation requires a team effort. Work closely with data scientists to understand the capabilities and limitations of AI models, and with developers to integrate AI features into your product.
Test and Iterate: AI is not a "set it and forget it" solution. Continuously test your AI-powered features with real users, gather feedback, and iterate on your designs.
Stay Updated: The field of AI is rapidly evolving. Keep learning about new tools, techniques, and best practices to stay ahead of the curve.
Prioritize Explainability: When using AI to make design decisions or personalize experiences, strive for transparency. Users (and definitely you! 😎) should have some understanding of why certain recommendations are made or why the interface behaves in a certain way. This can be achieved through clear communication and intuitive feedback mechanisms.
Design for Edge Cases: AI models are trained on data, and they may not always perform well in unusual or unexpected situations. Consider how your design will handle edge cases or scenarios where the AI might make mistakes. Provide clear error messages and graceful degradation paths to maintain a positive user experience.
Treat AI as a collaborative partner, and you can unlock new levels of creativity, efficiency, and user satisfaction. The goal is not to replace human designers but to augment them with tools that enhance their abilities and enable them to create truly exceptional experiences!
Questions Deepdive:
1️⃣ How can UX/UI designers ensure that AI-driven personalization enhances, rather than detracts from, the user experience, especially considering the risk of creating "filter bubbles" or echo chambers?
Implement transparent algorithms that allow users to understand and control their personalization settings.
Introduce serendipity elements or "wildcard" recommendations to expose users to content outside their usual preferences.
Regularly audit personalization algorithms for bias and unintended narrowing of user experiences.
2️⃣ Beyond current applications, what are some speculative yet plausible ways AI could revolutionize UX/UI design in the next 5-10 years?
Development of AI co-designers that can generate novel design ideas and collaborate with human designers in real-time.
Emergence of hyper-personalized interfaces that adapt not only to user preferences but also to their emotional states and cognitive load.
Creation of "living" design systems that continuously evolve based on real-world user interactions and feedback.
3️⃣ How can UX/UI designers effectively measure the impact of AI-driven features on user satisfaction and business outcomes?
Establish clear metrics for user engagement, task success, and conversion rates before implementing AI features.
Conduct A/B testing to compare user behavior with and without AI-driven elements.
Combine quantitative data with qualitative user feedback to gain a holistic understanding of AI's impact.
4️⃣ What strategies can UX/UI designers employ to ensure that AI-powered features are accessible to users with diverse abilities and needs?
Design AI systems that can adapt to various input methods (e.g., voice, gesture) and output formats (e.g., audio descriptions, haptic feedback).
Train AI models on diverse datasets that include users with different disabilities to avoid algorithmic bias.
Provide customizable accessibility settings that allow users to tailor the AI's behavior to their specific needs.
5️⃣ How can UX/UI designers collaborate effectively with data scientists and engineers to create ethical and user-centered AI-powered products?
Establish a shared language and understanding of key AI concepts, user needs, and design principles.
Engage in iterative prototyping and testing cycles that involve all team members.
Foster a culture of open communication and mutual respect, where designers, data scientists, and engineers can learn from each other.
6️⃣ What role can AI play in automating the more tedious aspects of UX/UI design, and how can designers ensure that this automation complements rather than stifles their creativity?
AI can automate tasks like asset organization, design system updates, and basic layout generation, freeing designers to focus on higher-level strategic thinking.
Designers can guide AI tools by setting constraints, providing creative direction, and curating AI-generated outputs.
Using AI as a "creative sparring partner" can lead to new ideas and perspectives that might not emerge through traditional methods alone.
7️⃣ In the context of predictive UX, how can designers strike a balance between anticipating user needs and respecting user agency and control?
Predictions should be presented as suggestions rather than mandates, allowing users to accept, reject, or modify them.
Provide clear explanations for why a particular prediction is being made, enhancing transparency and user trust.
Design interfaces that allow users to easily override AI predictions and take full control of their experience when desired.
8️⃣ How might AI-driven design tools change the skillset and educational needs of future UX/UI designers?
Future designers may need a stronger understanding of data science principles, AI ethics, and the capabilities/limitations of machine learning.
Educational programs might incorporate more interdisciplinary training, blending design thinking with technical skills related to AI implementation.
Soft skills like collaboration, critical thinking, and adaptability will become even more crucial in a rapidly evolving technological landscape.